Five-Step design process
- Initial design meeting
- Current-state analysis
- Stakeholder and SME training
- Design sessions
- Design deliverables
Project participants (SMEs / Key Stakeholders)
A design project manager has to determine a list of SMEs and project stakeholders who can provide information about the design requirements. This list typically includes:
- Network administrators
- Storage administrators
- Server hardware administrators
- Operating system administrators
- Application administrators
- Security Officer
- HR representatives
- C-Level executives (CEO, CTO, CIO,...)
- Representatives
It is important to lists the people involved in this project and their contact information. This list should include:
- Name
- Title
- Organisation
- E-Mail address
- Phone number
- Reachability
Having contact information available will help to make progress without unnecessary interruption during the design process.
Stakeholder = A person with an interest in a project
SME = A subject-matter expert is a person who is an expert in a particular area.#
Functional / Non-functional requirements
Functional requirements are tasks or processes that must be performed by the system. For example, a functional requirement of a vSphere platform is "must allow multi tenancy" or "users must be able to create virtual machines".
Non-functional requirements are standards that the system under must have or comply with. For example, a non-functional requirements for a vSphere platform is "must be built for a total cost of $500.000". Non-Functional requirements are also called constraints.
Conceptual design
The conceptual design typically focuses on the business requirements. It is an high level overview which includes only the most important components. Concept design is the first phase of the design process.
Conceptual design from an stretched Cluster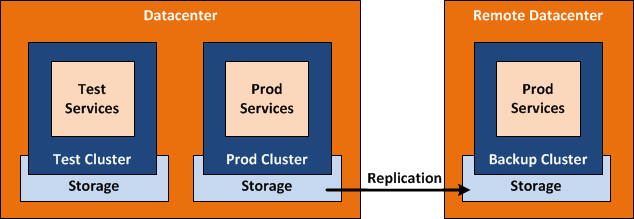
Conceptual design from a webservices platform
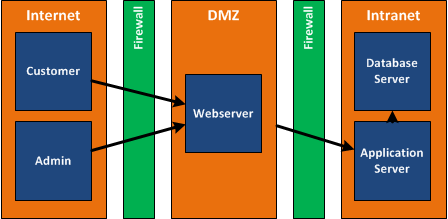
Logical design
The logical design specifies the relationship between all components. It is usually stable which means that it will only change if the requierement changes. The logical design does not include physical details such as IP addresses, hostnames or hardware models.
Physical design
The physical design is usually the last and the most specific design. It shows port connections, IP addresses and model description.
Requirement tracking
It is important to document all requirements. This could be done in an excel sheet for example. Every single requirement should contain at least a unique number, desciption, timestap, priority and the originator.
VCAP5-DCD Exam Blueprint v1.1
Skills and Abilities
- Associate a stakeholder with the information that needs to be collected.
- Utilize customer inventory and assessment data from a current environment to define a baseline state.
- Analyze customer interview data to explicitly define customer objectives for a conceptual design.
- Identify the need for and apply requirements tracking.
- Given results of a requirements gathering survey, identify requirements for a conceptual design.
- Categorize requirements by infrastructure qualities to prepare for logical design requirements.
Tools
Very informative material so far i have seen for VDCD 510.
Thanks :)
Pingback: VCAP5-DCD Objective 1.1 – Gather and analyze business requirements - VirtuallyHyperVirtuallyHyper
Pingback: VCAP5-DCD Objective 2.1 –Map Business Requirements to the Logical Design - VirtuallyHyperVirtuallyHyper